Types of Office Rental Costs in Vietnam: Full Breakdown

Renting office space is one of the key financial decisions for any business, because it not only impacts the brand image but also directly affects the long-term operational budget. However, many businesses still have an incomplete understanding of the types of office rental costs in Vietnam. This leads to inaccurate budgeting, additional expenses beyond the contract, or the inability to properly account for eligible office rental costs during tax settlement.
Table of Contents
- 1. What is Office Rental Cost?
- 2. 12 Common Types of Office Rental Costs in Vietnam
- 3. Guide to Calculating Total Office Rental Costs
- 4. Which Office Rental Costs Are Eligible for Accounting?
- 5. How to Record Office Rental Costs in Accounting Books
- 6. Regulations on Office Rental Costs Related to Taxes
- 7. Common Mistakes in Evaluating Office Rental Costs
- 8. Maison Office Supports Businesses in Optimizing Office Rental Costs
- 9. Frequently Asked Questions About Office Rental Costs
1. What is Office Rental Cost?
Office rental costs encompass all the expenses a business needs to pay in order to use and operate a workspace in a commercial office building. It is not just the rental rate per square meter, as many people mistakenly believe, but also includes various additional items related to operations, management, utilities, and legal matters.

For many businesses, having a thorough understanding of office rental cost Vietnam is key to:
– Developing an effective operational budget.
– Avoiding uncontrolled cost overruns.
– Ensuring that costs are properly accounted for in accordance with tax regulations.
“According to an internal survey conducted by Maison Office with over 500 clients in Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi, 47% of businesses reported that their actual total costs were 15 – 25% higher than the listed rental rate, primarily due to overlooked additional expenses or miscalculations in the contract terms.”
2. 12 Common Types of Office Rental Costs in Vietnam
When renting office space, many businesses focus solely on the rental rate per square meter without fully assessing the related costs. This can lead to budget discrepancies and impact overall financial efficiency.
In practice, the types of office rental costs in Vietnam are typically divided into 04 main categories: fixed costs, variable costs, one-time costs, and costs affected by contract terms.
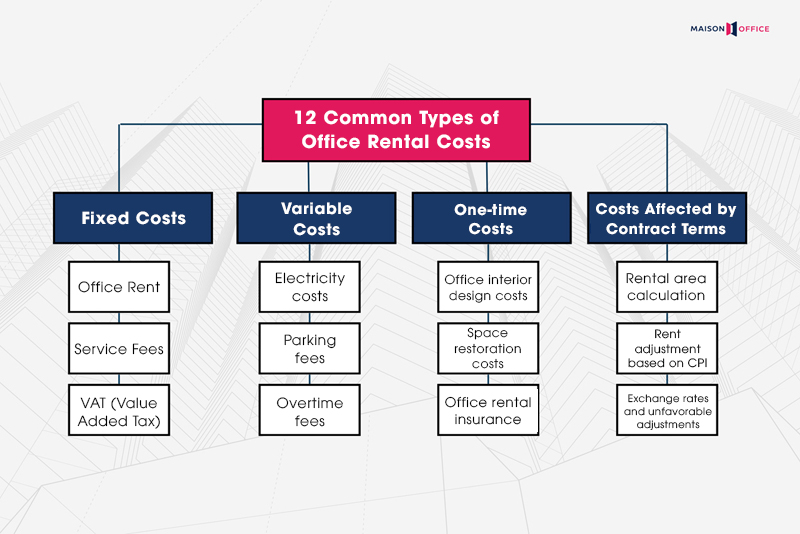
2.1 Fixed Monthly Costs
Fixed monthly costs are the mandatory and relatively stable payments throughout the office rental period, including:
– Office Rent: Calculated based on area (net usable area or wall-to-wall), with the unit price varying according to the building class (A, B, C) and geographical location.
– Service Fees: Covering costs for management, cleaning, maintenance of common systems, typically calculated per square meter (m2) per month.
– VAT (Value Added Tax): Applied at 10% on the total rent and service fees, in accordance with current tax regulations.
2.2 Variable Costs
These costs arise depending on the business activities and the extent of space utilization. They typically include:
– Electricity costs: Usually separate from service fees, calculated based on individual meters or the building’s specified unit price.
– Parking fees: Charged based on the number of motorcycles/cars registered by employees.
– Overtime fees: Many office buildings charge fees for working outside regular business hours or on weekends.
>> See more: After-Hours Office Rental Fees: What You Need to Know
2.3 One-time Costs
One-time costs occur at the beginning or end of the rental contract and can represent a significant portion of the total cost if not carefully considered. These include:
– Office interior design and construction costs: This includes design, construction, and finishing office space, typically not considered part of the rental cost but affects the overall budget.
– Space restoration costs: A mandatory expense when the contract ends if the space needs to be returned to its original condition.
– Office rental insurance: Some buildings require the purchase of property and fire insurance for the rented area.
2.4 Costs Affected by Contract Terms
These costs are often unclear unless carefully reviewed with proper consultation. Therefore, businesses need to carefully consider the following terms:
– Rental area calculation: The method used to calculate the rental area (wall-to-wall or net usable area) will impact the total cost.
– Rent adjustment based on the CPI index: Some contracts stipulate annual rent adjustments based on inflation (Consumer Price Index).
– Exchange rates and unfavorable adjustments: For contracts priced in USD but paid in VND, fluctuations in the exchange rate can lead to unforeseen additional costs.
3. Guide to Calculating Total Office Rental Costs
Instead of solely relying on the rental rate per square meter, businesses should evaluate office rental cost Vietnam based on the total actual expenses. These include: base rent, service fees, VAT, variable costs, one-time expenses, and contract adjustment factors such as CPI or exchange rates.
3.1 Formula for Monthly Office Rental Costs
|
Total monthly rental cost = (Rental rate + Service fees) * Rental area + 10% VAT + Electricity costs + Parking fees (based on quantity) + Overtime fees (if applicable) |
Example:
| Category | Unit | Unit Price (VND) | Notes |
| Rental Area | m2 | 100 | |
| Rental Price | VND/m2 | 450 | |
| Service Fees | VND/m2 | 120 | Applies to rent + service fees |
| VAT (10%) | % | 10 | |
| Air Conditioning | month | 3,000,000 | Estimated |
| Motorbike Parking Fee (5 bikes) | VND/bike/month | 200 | 1,000,000 |
| Total Monthly Cost (estimated) | VND/month | ~66,000,000 |
3.2 Calculating Initial One-time Costs
– Deposit fee: Typically 2 – 3 months of base rent
– Interior fit-out cost: Depending on design, around 2 – 5 million VND/m2
– Restoration cost: Applicable if there’s a commitment to return the space to its original condition
– Office insurance fee: If required by the building
These are not part of the monthly fees but directly impact the total budget in the first year.
3.3 Estimating Total Rental Costs over 12 Months
| First-year total rental cost = (Monthly rental cost * 12 months) + Fit-out cost + Deposit fee + Restoration cost (if applicable) |
Suggestion: Businesses should create a detailed Excel spreadsheet outlining each cost item to assess financial capacity and compare different leasing options effectively.
4. Which Office Rental Costs Are Eligible for Accounting?
For businesses, office leasing is not just an operational issue – it also directly impacts deductible expenses when determining corporate income tax (CIT). However, not all office rental-related costs are considered eligible deductible expenses.
Office rental costs are considered eligible deductible expenses if they meet the following 03 conditions (as stipulated in Circular 96/2015/TT-BTC):
| Condition | Description |
| For business operation purposes | The rented office must serve the business’s revenue-generating or operational activities. |
| Supported by valid invoices and legal documents | Includes: lease contract, financial invoice (or tax receipt if renting from individuals), and non-cash payment evidence (for payments over 20 million VND). |
| Not classified as restricted or non-deductible | For example: expenses exceeding allowable limits, rental of non-existent “virtual” offices, or lacking valid supporting documents. |
Common office rental expenses considered deductible:
– Office rent as specified in the lease agreement
– Building management service fees (if clearly stated in the contract and invoice)
– Input VAT (if eligible for deduction)
– Electricity, water, and overtime charges (with valid invoices)
– Depreciation of office furniture and fixtures invested by the business
– Restoration costs (if contractually required upon lease termination)
Cases where office rental costs are NOT considered deductible:
– Renting an office without a valid lease agreement or invoice
– Rent payments made in cash exceeding 20 million VND per transaction
– “Virtual offices” used solely for business registration without actual usage
– Interior expenses that exceed allowable depreciation or are not properly allocated
For examples:
– A business rents an office for 30 million VND/month with a valid contract, VAT invoice, and bank transfer → 100% deductible expense.
– Renting an office from an individual for 6 months without a contract and paid in cash → Not deductible.
5. How to Record Office Rental Costs in Accounting Books
To ensure office rental expenses are properly recognized and deductible for corporate income tax purposes, businesses must accurately account for these costs in compliance with Vietnamese accounting standards and current regulations, including Circular 200/2014/TT-BTC and Circular 96/2015/TT-BTC.
Depending on the payment method (prepayment, post-payment, or periodic payments), office rental expenses should be recorded in the appropriate accounts such as 242, 335, 154, 627, 641, 642, etc.
5.1 Accounting for Full Advance Payment of Rental Costs
This method applies when the business pays the full rental amount under the contract at the beginning of the term.
Debit Account 331 – Payables to lessor
– Credit Account 111, 112 – Cash or bank transfer
5.2 Accounting for Advance Payments for Multiple Periods (Prepaid Expenses)
When a company makes a one-time payment for 6 months to 1 year of rent, the expense must be allocated evenly each month.
Accounting entry upon receiving the invoice:
Debit Account 242 – Long-term prepaid expenses
Debit Account 133 – Input VAT (if applicable)
– Credit Account 111, 112, or 331 – Cash, Bank Transfer, or Payables
Monthly Allocation Accounting Entry:
Debit Account 154, 627, 641, or 642 (depending on usage purpose)
– Credit Account 242 – Prepaid expenses
5.3 Accounting for Monthly Rental Payments
This method is used when the business pays or receives the office rental invoice on a monthly basis.
Debit Accounts 154, 627, 641, 642 – Operating expenses
Debit Account 133 – Input VAT (if any)
– Credit Accounts 331, 111, 112 – Payables or immediate payment
5.4 Accounting for Post-Payment (or Upon Receiving Invoices)
Example: The company rents the office from January to June but only receives the invoice or makes payment to the lessor in July.
Monthly expense recognition entry (even if unpaid):
Debit Account 154, 627, 641, 642 – Operating expenses
– Credit Account 335 – Accrued expenses
When payment is made or an invoice is received:
Debit Account 335 – Accrued expenses
– Credit Account 111, 112 – Cash or bank transfer (upon payment)
Debit Account 331 – Payables (if a VAT invoice is issued)
6. Regulations on Office Rental Costs Related to Taxes
When renting an office, in addition to calculating rental rates and operating costs, businesses must pay close attention to tax considerations to ensure expenses are recognized as deductible. A lack of understanding of tax regulations may lead to disallowed expenses or penalties. Below are 3 key types of taxes to note:
>> See more: Office rental tax rate 8 or 10? Can VAT be reduced?
6.1 Conditions for VAT Deduction on Office Rental Costs
Value Added Tax (VAT) is a common tax that businesses are required to pay when leasing office space from legally recognized lessors (i.e., organizations with legal entity status).
When leasing office from a registered business or organization, the tenant will receive a VAT invoice with a standard tax rate of 10% applied to the total rental fee plus service charges. This VAT amount can be deducted if the business meets the legal requirements, including:
– Having a clear and valid lease agreement
– A legitimate VAT invoice from the lessor
– Payment made via bank transfer if the amount exceeds 20 million VND
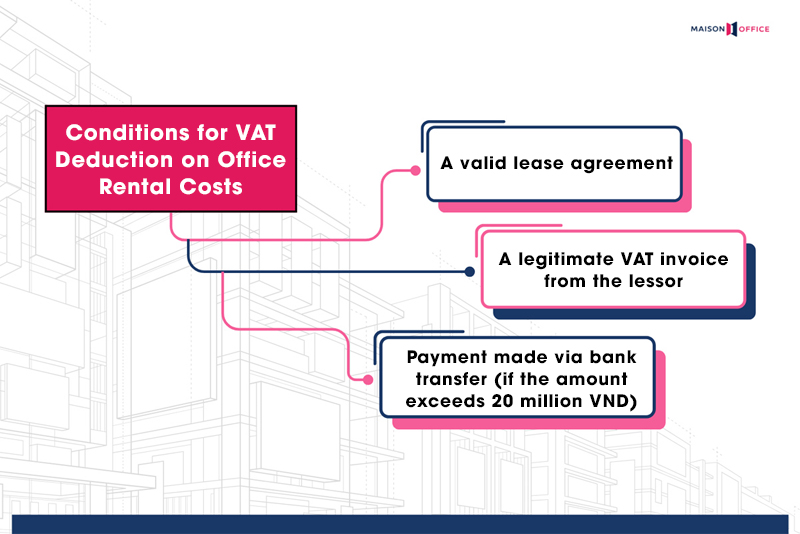
Note: In cases where the lease is from an individual who does not issue a VAT invoice, the business cannot deduct this tax.
6.2 Personal Income Tax (PIT) for Individual Landlords
When a business rents office space from an individual, the lessor must pay personal income tax (PIT) and VAT if the total rental revenue exceeds 100 million VND per year. In this case, the business is obligated to:
Withhold and pay on behalf of the lessor:
– VAT: 5%
– Personal Income Tax (PIT): 5%
Prepare a clear lease agreement, declare and pay taxes on time
Properly record the rental expense in the accounting books
Note: If an individual’s rental income is under 100 million VND per year, they are exempt from all 03 taxes: VAT, personal income tax (PIT), and business license tax.
6.3 Periodic Tax Declaration Requirements for Office Rental Costs
To ensure office rental costs are recognized as valid expenses and not disallowed during tax finalization, businesses must:
– Declare in the correct accounting period (monthly or quarterly)
– Keep complete invoices, contracts, and payment documents
– Declare input VAT (if deductible)
– Declare and pay taxes on behalf of individuals (if renting from individuals)
Timely tax declaration and payment also help avoid errors and administrative tax violations.
7. Common Mistakes in Evaluating Office Rental Costs
Many businesses, especially startups or first-time office renters, often underestimate the full range of actual costs. This can easily lead to budget overruns, affecting operational efficiency and long-term financial planning.
Here are 5 common mistakes businesses should avoid:
– Focusing only on the rental rate per m2 and overlooking additional costs such as VAT, service fees, electricity cost, parking fees, etc.
– Failing to review lease price adjustment clauses in the contract carefully.
Not negotiating one-time costs or annual rent increase rates thoroughly.
– Misunderstanding how the leased area is calculated (gross vs. net), leading to inaccurate total cost estimates.
– Not preparing a comprehensive rental cost summary for comparison and budgeting.
Suggestion: Before signing the office lease, businesses should create a detailed Vietnam office lease cost breakdown and compare options across buildings. If needed, Maison Office can help you analyze rental costs, negotiating lease terms, and review contracts.
>> See more: What’s the difference between Net area vs Gross floor area?
8. Maison Office Supports Businesses in Optimizing Office Rental Costs
With over 10 years of experience advising and representing tenants in negotiations with landlords in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City, Maison Office not only helps businesses find the right workspace but also supports them throughout the negotiation process to optimize total rental costs.
Here are 5 ways Maison Office can help your business save time, budget, and reduce unexpected risks:
Transparent and comprehensive cost consultation
– Analyze total rental costs: base rent, service charges, VAT, parking fees, after-hours usage, fit-out costs, reinstatement fees, etc.
– Provide clear monthly and yearly cost estimates to avoid being misled by low rent offers with unexpected extra fees.
Compare rental costs across buildings in the same segment
– Maison Office maintains a database of 2,000+ office buildings in central districts.
– We help clients compare actual rental costs, chargeable areas, and incentives such as free fit-out or parking.
Negotiating contract terms favorable to cost
Support negotiations on terms such as:
– Waiving overtime fees, waiving charges based on vehicle quantity, etc.
– Offering 1 – 3 months of free rent for office interior design activities.
– Limiting periodic rent increases
Carefully reviewing clauses on CPI adjustments, exchange rates, and premises handover to avoid unexpected costs after contract signing.
Representing business in negotiations with building owners
– Save time by avoiding multiple 1:1 meetings with different landlords.
– Ensure the business secures the best leasing terms aligned with a clear budget and usage requirements.
Legal and accounting support related to rental costs
– Guide the preparation of contracts, invoices, and payment documents to ensure valid expense recognition for tax finalization.
– Coordinate with the company’s finance department to handle rental cases involving individuals, VAT deductions, and personal income tax declarations.
Maison Office is not just an office space provider but a strategic partner that helps businesses make smart, cost-effective, and legally compliant leasing decisions – from cost analysis to contract signing.
Contact Maison Office now for free consultation and a cost comparison of office rentals in your areas of interest.
9. Frequently Asked Questions About Office Rental Costs
Is an invoice mandatory for office rental costs?
Yes. To recognize office rental as a valid expense for corporate income tax finalization, the company must have a full financial invoice, lease contract, and non-cash payment evidence (if payment exceeds 20 million VND per transaction). Without an invoice, the expense will be disallowed.
Can office rentals from individuals without an invoice be eligible costs?
Yes, but compliance with regulations is required. The company must sign a clear lease contract and withhold/pay personal income tax (5%) and VAT (5%) if the individual’s annual rental income exceeds 100 million VND. Failure to follow these procedures may lead to disallowance of the expense during tax audits.
Can office interior construction costs be included as allowable expenses?
Yes, if the costs serve business activities and are properly allocated or depreciated over their useful life. Large expenses for interior work usually must be capitalized as fixed assets and depreciated according to tax regulations.
Can businesses deduct VAT from office rental costs?
Yes, if renting from an organization issuing valid VAT invoices and payments are made via bank transfer. If renting an office from individuals without VAT invoices, VAT cannot be deducted.
Is a notarized contract required for office rentals?
No, it is not mandatory. Under current law, commercial office lease contracts do not require notarization as long as both parties clearly agree and the contract is legally signed. However, notarization is recommended for long-term leases to enhance legal certainty.

Editor and content team manager at Maison Office.
With over 5 years of experience in consulting and extensive content editing in the real estate services and interior design field. Sharing valuable information with customers, partners, and attracting millions of views.




