What is an I-REC? The benefits of renewable energy certificates

The green energy transition is not only a trend but also a mandatory requirement for businesses in the era of sustainable development. One of the most important tools to demonstrate this commitment is the I-REC (International Renewable Energy Certificate) – a global certification system for 1 MWh of renewable electricity generated and consumed. With its growing role in ESG strategies, I-REC provides businesses with benefits in terms of branding, finance, and access to international markets.
Table of Contents
- 1. What is an I-REC?
- 2. Types of I-REC Renewable Energy Certificates
- 3. Benefits of Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs)
- 4. How are Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) created?
- 5. Registering and Purchasing I-RECs in Vietnam
- 6. REC Markets Worldwide and in Vietnam
- 7. Distinguishing Between I-RECs and Carbon Credits
- 8. FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about I-RECs
1. What is an I-REC?
An I-REC (International Renewable Energy Certificate) is an internationally recognized renewable energy certificate that certifies one unit of electricity (1 MWh) generated from renewable sources such as solar, wind, or hydropower. I-RECs enable companies and organizations to demonstrate their commitment to clean energy consumption, reduce Scope 2 emissions in line with the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol, and enhance credibility by ensuring transparency of energy sources in ESG reporting.

The I-REC system is designed to create a transparent and standardized mechanism for tracking, certifying, and trading renewable electricity in countries that do not yet have a national certification program. Each I-REC not only records the volume of renewable electricity generated but also includes detailed information such as:
- Generation technology type (solar, wind, hydro, etc.)
- Location and time of production
- Project capacity and associated emission factors

I-REC holders have the legal right to claim the use of renewable energy, thereby reducing Scope 2 emissions in ESG reporting and meeting international standards such as RE100, CDP, the GHG Protocol, and ISO 14064.
Today, I-RECs have been implemented in more than 50 countries and have become one of the most widely adopted instruments for enabling companies worldwide to pursue Net Zero strategies and strengthen their brand credibility.
2. Types of I-REC Renewable Energy Certificates
Within the global EAC (Energy Attribute Certificates) system, I-RECs are renewable energy certificates applied in countries that do not have their own certification schemes. In essence, I-RECs are not divided into multiple variants, but they can be categorized based on the renewable generation technology, including:
- Solar I-REC: certifies the electricity generated from solar power projects.
- Wind I-REC: applies to both onshore and offshore wind projects.
- Hydropower I-REC: covers electricity produced from large-scale as well as small and medium-sized hydropower projects.
- Biomass/Biogas I-REC: certifies electricity generated from organic waste or biogas.
- Geothermal I-REC: issued for projects that generate electricity from geothermal resources.

In addition to I-RECs, there are other certification mechanisms on the international market that also fall under the EAC (Energy Attribute Certificates) category, specifically:
- GO (Guarantee of Origin): certificates used within the European Union.
- REC (Renewable Energy Certificate): applied in the United States and Canada.
- TIGR (Tradable Instrument for Global Renewables): issued by APX, enabling the creation, verification, and transparent trading of renewable energy certificates on a digital platform.
3. Benefits of Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs)
Owning renewable energy certificates (RECs, including I-RECs, GOs, TIGRs, etc.) delivers significant value to businesses, communities, and the energy market as a whole.
Key benefits of RECs for businesses:
- Proof of renewable energy consumption: RECs provide transparent evidence that the electricity consumed originates from clean energy sources.
- Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 2): RECs help companies meet Net Zero commitments and comply with international environmental standards such as the GHG Protocol, RE100, and CDP.
- Enhanced brand reputation: RECs create a competitive edge with partners, investors, and environmentally conscious consumers.
- Access to international markets: Many multinational corporations require their suppliers to hold renewable energy certification.
- Improved access to green finance: Companies with I-RECs strengthen their ESG reports, making them more attractive to green investors and funding opportunities.

Benefits of Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) for energy producers:
- Increased revenue: In addition to income from selling electricity, renewable energy projects generate extra income through REC trading.
- Shorter payback period: Additional revenue streams create stronger incentives for new investments in clean energy.
Benefits of Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) for society and the environment:
- Encouraging the green energy transition: RECs promote higher adoption of renewable energy within national power systems.
- Contributing to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): particularly SDG 7 (affordable and clean energy) and SDG 13 (climate action).
4. How are Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) created?
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) are generated through a rigorous process designed to verify and separate renewable electricity production from other energy attributes (such as commercial electricity or carbon credits).

The creation process of RECs generally involves the following steps:
- Step 1: Renewable electricity generation
- Solar, wind, hydropower, biomass, and geothermal plants generate electricity and feed it into the grid.
- For every 1 MWh of renewable electricity produced, the plant is eligible to issue 1 REC.
- Step 2: Data recording and verification
- Electricity generation is measured through reliable metering systems.
- The data is verified by an independent third party to ensure accuracy and transparency.
- Step 3: Registration and issuance
- Generation data, including technology type and production location, is submitted to a recognized registry (e.g., I-REC Standard Foundation, Evident Services).
- The registry issues an electronic certificate, each with a unique identifier.
- Step 4: Trading and transfer
- RECs can be bought and sold on the voluntary market or through official exchanges.
- Electricity consumers purchase RECs to demonstrate renewable energy use in ESG and sustainability reporting.
- Step 5: Cancellation (Redemption)
- Once used for reporting, RECs are permanently cancelled in the registry to ensure they cannot be reused.
- This prevents “double counting” of environmental benefits and maintains system integrity.
Through this mechanism, RECs provide transparency and allow companies to credibly demonstrate their clean energy commitments without directly purchasing electricity from renewable plants.
5. Registering and Purchasing I-RECs in Vietnam
In Vietnam, the demand for proving renewable energy consumption is increasing, especially following the country’s Net Zero commitments. The International Renewable Energy Certificate (I-REC) has become a transparent tool for companies to meet international standards such as ESG, RE100, and CDP, while enhancing their brand credibility in global markets.
To register and purchase I-RECs, companies can follow these steps:
- Register renewable energy projects: Solar, wind, hydropower, and biomass plants must register with the I-REC Standard Foundation or through authorized partners.
- Verification and issuance: Renewable electricity output is measured and verified by an independent third party, then converted into electronic I-RECs (1 I-REC = 1 MWh).
- Trading and procurement: Companies can purchase I-RECs directly on international exchanges or through local distributors in Vietnam. Alena Energy, the official partner of I-REC Standard, is a pioneer in supplying I-RECs to major corporations such as Samsung, LG, Foxconn, IKEA, and Microsoft.
- Certificate redemption (cancellation): Once used for ESG reporting, I-RECs are permanently cancelled to ensure transparency and prevent double counting of environmental benefits.
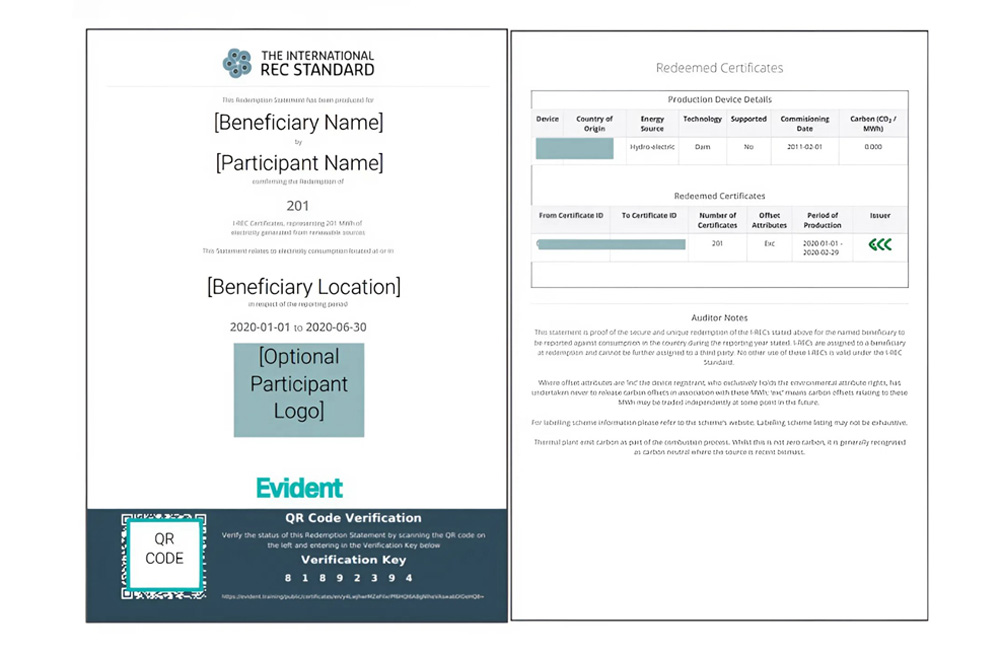
Benefits of owning I-RECs in Vietnam:
- Enable companies to demonstrate renewable energy consumption and meet requirements from global partners.
- Facilitate access to demanding export markets, particularly in Europe.
- Enhance competitiveness and attract green investment capital.
- Support Vietnam’s national goals of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable development.
With a stable distribution system, diverse supply sources, and a team of experienced experts, Alena Energy is regarded as the most trusted partner for companies seeking to register and purchase I-RECs in Vietnam.
6. REC Markets Worldwide and in Vietnam
6.1 Global REC Market
The global Renewable Energy Certificate (REC) market is entering a phase of strong growth, driven by the rising demand for clean energy and supportive government policies. According to forecasts by the International Energy Agency (IEA), the REC market could reach a value of USD 300 billion by 2030.
- Leading regions: North America and Europe currently hold the largest market shares. The United States and Canada operate their own REC systems, while the European Union uses the Guarantee of Origin (GO) mechanism.
- Energy type segmentation: Solar RECs account for the largest share, followed by wind and hydropower.
- Main applications: Compliance with regulatory requirements, carbon offsetting (Scope 2 emissions), and participation in energy trading.
- Key trends: Increased investment in renewable energy, stronger government incentives, rising demand for carbon offsets, and market expansion in emerging economies.
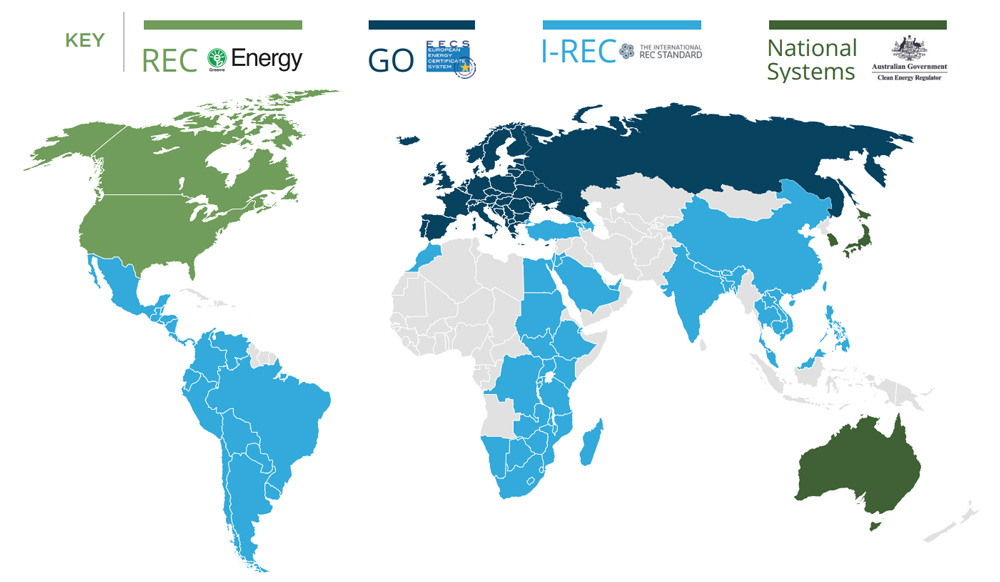
In particular, the International Renewable Energy Certificate (I-REC) is becoming the recognized standard in many countries. As of August 2023, more than 512.33 million I-RECs had been issued, representing 195.2 GW of renewable capacity, with over 4,200 projects across 48 countries being certified.
6.2 REC Market in Vietnam
In Vietnam, the REC/I-REC market is still relatively new but has been growing rapidly in line with the country’s green energy transition. According to estimates by the Ministry of Industry and Trade (MOIT), the REC market in Vietnam could reach a value of USD 1 billion by 2030.
- Market composition: Solar RECs account for the largest share, followed by hydropower and wind power.
- Main applications: ESG reporting, regulatory compliance, and participation in international energy trading.
- Project scale: As of October 2023, Vietnam had 492 projects certified with I-RECs, with a total capacity of over 8,000 MW, including:
- 353 solar power projects
- 124 hydropower projects
- 15 wind power projects
- TIGR in Vietnam: There are currently 196 projects certified under the TIGR system, with a total capacity of over 864 MW, primarily from solar power.
- Issuing body: I-RECs in Vietnam are administered by the I-REC Standard Foundation through an authorized independent local entity.
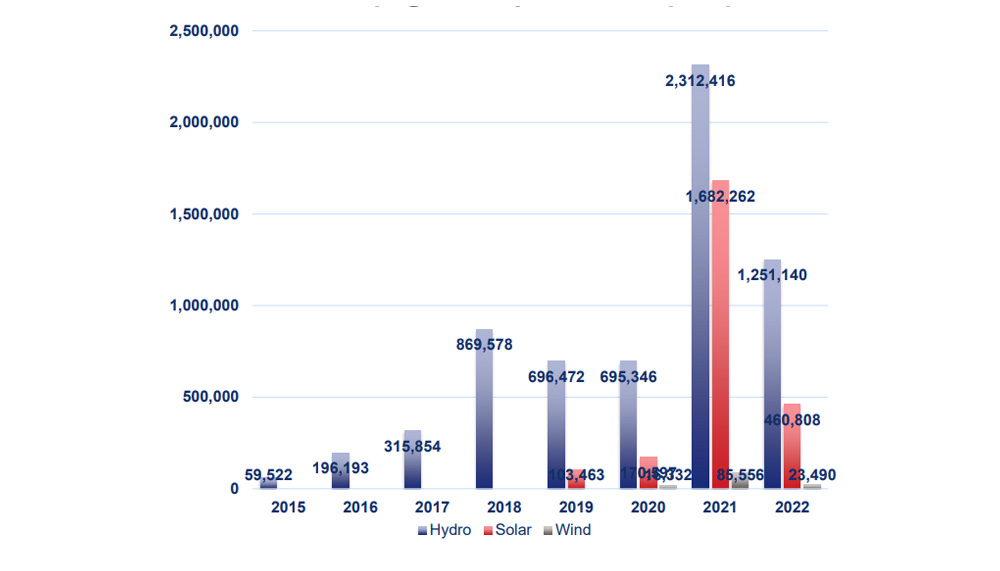
Future trends indicate that the demand for I-RECs in Vietnam will continue to grow strongly due to:
- The rapid expansion of solar and wind power.
- The Government’s Net Zero 2050 commitment.
- Increasing pressure from export markets, particularly in Europe and the United States, requiring proof of renewable energy consumption across supply chains.
Vietnam is emerging as a promising I-REC market in Asia, not only fostering investment in renewable energy but also creating opportunities for green financing for businesses.
7. Distinguishing Between I-RECs and Carbon Credits
In sustainability strategies, many companies often confuse International Renewable Energy Certificates (I-RECs) with Carbon Credits. In reality, these are two distinct instruments that differ in nature, creation, and purpose of use.
- I-REC (International Renewable Energy Certificate): certifies that renewable electricity has been generated and fed into the grid.
- Carbon Credit: certifies that a certain amount of CO₂ or other greenhouse gases has been reduced or removed from the atmosphere.
| Criteria | I-REC (International Renewable Energy Certificate) | Carbon Credit |
| Nature | Certifies 1 MWh of renewable electricity generated and fed into the grid. | Certifies 1 ton of CO₂e reduced or removed. |
| Purpose | Demonstrates the use of renewable energy (reducing Scope 2 emissions). | Offsets greenhouse gas emissions from company activities (reducing Scope 1 and Scope 3 emissions). |
| Source | Renewable power plants: solar, wind, hydropower, biomass, geothermal. | Emission reduction projects: afforestation, renewable energy, methane capture, energy efficiency. |
| Measurement unit | 1 I-REC = 1 MWh of renewable electricity. | 1 Carbon Credit = 1 ton CO₂e (carbon dioxide equivalent). |
| Main application | ESG reporting, RE100, CDP, proof of clean energy use. | Compliance with regulatory markets (compliance market) or voluntary offsetting (voluntary market). |
| Market | Mainly in countries without a national REC system (Asia, Latin America, Africa). | Available in both compliance and voluntary markets worldwide. |
| Impact | Encourages investment in and consumption of renewable energy. | Contributes to reducing global greenhouse gas emissions. |
In summary:
- I-RECs enable companies to demonstrate renewable electricity consumption, making them suitable for ESG and Net Zero (Scope 2) targets.
- Carbon Credits allow companies to offset direct emissions, aligning with regulatory compliance obligations or comprehensive emission reduction commitments.
Overall, I-RECs are not only a transparent tool for verifying clean electricity use but also a strategic lever for enhancing brand credibility, meeting international ESG standards, and supporting Net Zero strategies. As both the global and Vietnamese REC markets continue to grow rapidly, understanding the nature, benefits, and registration process of I-RECs will help businesses take a proactive role in their sustainability journey.
To seize opportunities and optimize costs when participating in the I-REC market, companies should partner with authorized and reputable providers to ensure transparency, safety, and efficiency in transactions. This is a practical step for Vietnamese enterprises to strengthen their position, expand into international markets, and contribute actively to the global green energy transition.
8. FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about I-RECs
8.1 How long is an I-REC valid?
Each I-REC is issued to represent the generation of 1 MWh of renewable electricity within a specific time period. Once it is redeemed/cancelled, the certificate becomes permanently invalid and can no longer be traded.
8.2 Where can companies register for I-RECs?
Businesses can register directly with the I-REC Standard Foundation or through authorized partners in Vietnam such as Alena Energy or VNEEC. The process requires technical documentation, verification of generation data, and third-party validation to ensure accuracy and credibility.
8.3 Do small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) need I-RECs?
Although I-RECs are not mandatory, SMEs are strongly encouraged to obtain them. Holding I-RECs helps enhance corporate branding, demonstrate commitment to renewable energy, and meet the sustainability requirements of larger supply chain partners that are increasingly focused on ESG criteria.

Editor and content team manager at Maison Office.
With over 5 years of experience in consulting and extensive content editing in the real estate services and interior design field. Sharing valuable information with customers, partners, and attracting millions of views.



