What is LEED? LEED Standards in Office Buildings

In recent times, Maison Office has received numerous inquiries about LEED and the evaluation process of this certification system.
In today’s article, we will delve deeper into the LEED certification: What value does this certificate bring to buildings? How does the LEED standard system work? What are some notable projects around the world that have achieved LEED certification? Let’s explore the details together!
Table of Contents
- 1. What is leed?
- 2. LEED standard classification
- 3. Objectives of the LEED system
- 4. The role of LEED for businesses, people and the environment
- 5. Benefits and limitations of LEED standards
- 6. LEED Standard System
- 7. Differences Between LEED and Other Standards
- 8. Some Architectural Projects Following LEED Standards
1. What is leed?
LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) is a certification awarded by the U.S. Green Building Council, a non-governmental organization that evaluates buildings and projects for environmental friendliness.
The LEED standards are among the most widely recognized green building certifications globally. Buildings follow LEED certification to set environmental standards, including creating green spaces within real estate projects, while still ensuring the budget requirements set by the contractor are met.
Due to its popularity, many businesses have chosen LEED-certified buildings for their headquarters and offices worldwide. Vietnam is no exception, with several major buildings achieving this certification, such as the ATAD Dong Nai factory office, Johnson & Johnson Vietnam office, and the Capital Place twin towers.
See more about global green building certifications:
- LEED Certified
- WELL Certified
- Green Mark certification
- LOTUS certification
- EDGE certification
- Green Star certification
2. LEED standard classification
To achieve LEED certification, architectural projects must meet all prerequisite conditions and earn points across various levels. The higher the points, the more sustainable and environmentally friendly the real estate project is compared to others. The certification levels of the LEED standard typically follow these thresholds:
- LEED Certified standard: 40–49 points
- LEED Silver standard: 50–59 points
- LEED Gold standard: 60–79 points
- LEED Platinum standard: 80+ points
3. Objectives of the LEED system
LEED-certified buildings play a crucial role in addressing climate change and meeting ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals, promoting resilience and supporting fairness within communities. LEED does not focus solely on one specific aspect of building, such as energy, water, or health, but evaluates holistically to optimize every aspect and create the best possible building projects. The main goals of LEED include:
- Reducing contributions to global climate change.
- Enhancing individual human health.
- Protecting and restoring water resources.
- Protecting and enhancing biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- Promoting sustainable and renewable materials cycles.
- Improving community quality of life.
It is noted that in the LEED rating system, 35% of the categories focus on climate change, 20% directly impact human health, 15% affect water resources, 10% are related to biodiversity, 10% influence the green economy, and 5% impact the community and natural resources.
Furthermore, in LEED v4.1, many LEED categories are closely related to carbon and its presence. LEED categories also contribute to meeting the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), creating a positive interaction between LEED and SDGs.
4. The role of LEED for businesses, people and the environment
LEED is a prestigious certification system, recognized worldwide. Applying LEED standards in construction will bring many benefits to businesses, people and the environment.
4.1. For Businesses
LEED-certified buildings not only have a higher resale value but also incur lower operating costs compared to non-LEED buildings. Thus, LEED is not just an important strategy for achieving ESG goals, reducing carbon emissions, and promoting sustainability, but it is also a decisive factor in creating sustainable assets for investors, tenants, and communities.
4.2. For People
LEED-certified buildings focus particularly on the health of occupants, creating a cleaner, healthier, and more appealing environment, while addressing community and environmental health issues.
Additionally, the LEED rating system emphasizes strategies such as smoking bans and reducing exposure to toxins from building materials, aiming to improve indoor air quality.
4.3. For the Environment
Buildings that meet LEED standards can save energy and water, utilize renewable energy sources, and use resources more efficiently. This leads to less waste and ensures the conservation of land and habitats. Therefore, LEED certification is not just a specific solution but also a global partner for cities, communities, and their surrounding areas.
By promoting sustainable design, construction, and operational management according to LEED standards, it contributes to reducing carbon emissions, energy consumption, and waste, along with conserving water resources. Additionally, LEED prioritizes the use of safe materials and reduces exposure to harmful substances, contributing to comprehensive environmental protection.
5. Benefits and limitations of LEED standards
When constructing buildings according to LEED certification, investors and construction contractors can receive various benefits, specifically:
5.1 Advantages of LEED
- LEED certification is recognized in many countries, including the United States. Meeting stringent standards can be a factor for large businesses and multinational corporations to choose your site for their headquarters and offices.
- Environmentally friendly buildings that meet international standards are an extremely effective way to promote the project to the public, enhancing the image and status of investors and construction contractors to partners, customers, suppliers, and the public.
- Constructing a LEED-certified real estate project is also a way for businesses to meet government requirements and those of government agencies and organizations regarding environmental protection and sustainable development.
5.2 Disadvantages of LEED
Despite the outstanding advantages, the LEED standard also brings some limitations to contractors and investors:
- Meeting the requirements and regulations to achieve LEED certification requires businesses to spend more in the design, construction, and maintenance phases of real estate projects. This makes the office rental prices of LEED-certified real estate projects often higher than the market average.
- Some regulations related to the LEED standard may not be suitable for the specifics of Vietnam. This is why many investors strive for their projects to meet both LEED and LOTUS standards.
Despite some drawbacks, with its benefits, the LEED standard remains one of the popular green building evaluation systems in Vietnam. As of the end of 2018, there were 53 projects in Vietnam that had achieved LEED certification, according to the Ministry of Construction.
6. LEED Standard System
In the next section, we will learn more about the LEED standard system. The following information will hopefully help you understand how your real estate project can meet the stringent requirements of the LEED standard.
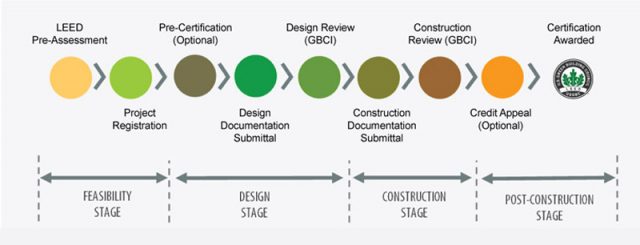
6.1 How LEED Certification Works
LEED Certification consists of prerequisite conditions and credits. Prerequisites are mandatory elements that any green building project must have to receive LEED certification. Credits are optional elements that investors can choose to increase the LEED score of their project.
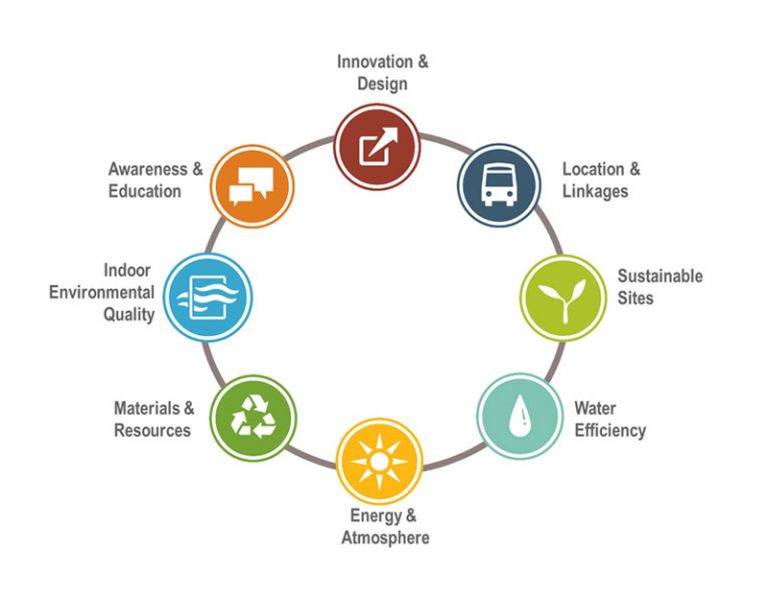
Although the prerequisites and credits for each architectural project can vary slightly (depending on the type of building and the related rating system), the common evaluation factors to meet the LEED standard include:
- Location and the surrounding transportation system.
- Energy usage.
- Resource and material usage during construction.
- Indoor environmental quality.
- Arrangement of green spaces within the building. The LEED evaluation system has been updated several times. After 2016, construction projects must meet the standards mentioned in LEED v4.
6.2 LEED Certification Standards
Standards for green buildings:
- LEED standard for new construction.
- LEED standard for core and shell.
- LEED standard for schools.
- LEED standard for retail (both new construction and renovation).
LEED standard for healthcare facilities. Standards for interior spaces:
- LEED standard for commercial interior spaces (offices, residences…).
- LEED standard for retail interiors. Standards for existing buildings:
- LEED standard for building operations and maintenance. Standards for neighborhoods:
- LEED standard for neighborhood development. Standards for homes:
- LEED standard for homes.
7. Differences Between LEED and Other Standards
Currently, in addition to LEED, architectural projects in Vietnam also follow other green building standards such as Green Mark, Green Star, or LOTUS. Let’s briefly review some of these green building certifications:
7.1 LOTUS
LOTUS is a certification system for green buildings and architecture, issued by the Vietnam Green Building Council (VGBC) and the World Green Building Council (WorldGBC). This standard’s uniqueness lies in its consultation, comparison, and establishment of standards according to the laws and building regulations in Vietnam.
Construction contractors often strive to meet both LEED and LOTUS standards in the process of constructing and completing their projects.
7.2 EDGE
EDGE is a standard system provided by the International Finance Corporation (IFC), part of the World Bank, to assess the sustainability and environmental friendliness of real estate projects. Currently, the EDGE certificate is recognized in many countries around the world, and in Vietnam, there are a total of 13 architectural projects that meet this standard (as of the end of 2018, according to the Ministry of Construction).
7.3 Green Mark
Green Mark is a certification issued by the Building and Construction Authority of Singapore to enhance the awareness of architectural project owners in constructing and building sustainable and environmentally friendly buildings and real estate projects.
This is considered one of the first green architecture standards established in Southeast Asia. Standards are collated and assessed against Singapore laws and regulations.
7.4 Green Star
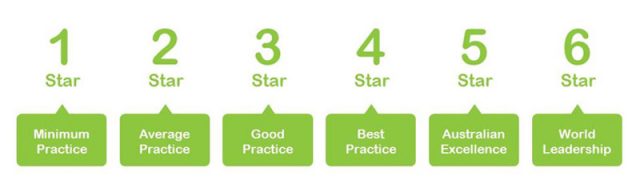
Green Star is a green building rating system evaluated by the Green Building Council of Australia. Unlike other certification systems, Green Star assesses the environmental friendliness of real estate projects through a star rating system from 0 to 6 (equivalent to the level from least to most environmentally friendly).
To align with other rating systems, each star corresponds to a specific score range (for example, scoring above 75 points is equivalent to achieving 6 stars according to Green Star).
Additionally, there are other green building and architecture rating systems applied worldwide, such as NatHERS and NABERS. Essentially, the assessment of a real estate project’s environmental friendliness is consistent across all rating systems. The main differences lie in the assessing body, the country in which the rating organization is based, and some local regulations.
Due to the presence of various standards, construction companies and investors should consider choosing a rating system that is recognized by many countries and territories.
8. Some Architectural Projects Following LEED Standards
We will introduce you to a few notable architectural projects that have earned LEED certification, both internationally and in Vietnam.
8.1 Manitoba Hydro Place – Canada
Manitoba Hydro Place in Canada is one of the most environmentally friendly office towers in North America and is the only architectural project to have received a LEED Platinum certification in Canada.
Located in
Winnipeg, Canada, it features 22 above-ground floors and 2 underground levels, reaching a height of 115 meters (to the roof). This office tower utilizes its south-facing roof to place solar panels, thereby generating renewable energy without harming the environment. Additionally, Manitoba Hydro Place exploits glass as a primary material to maximize natural light from the outside.
8.2 Apple Park – USA
In 2016, Apple’s office complex, Apple Park, received the LEED Platinum certification from the U.S. GBC.
This achievement reflects Apple’s effort to operate entirely on renewable energy. It is estimated that the solar panels on the office roof can produce up to 17 megawatts, covering up to 75% of the electricity demand during peak hours at the corporate headquarters.
The vast 71-hectare Apple Park complex offers various amenities such as cafes, plazas, parks, sports facilities, a hospital, and a memorial area (including an exhibition space and an Apple Store).
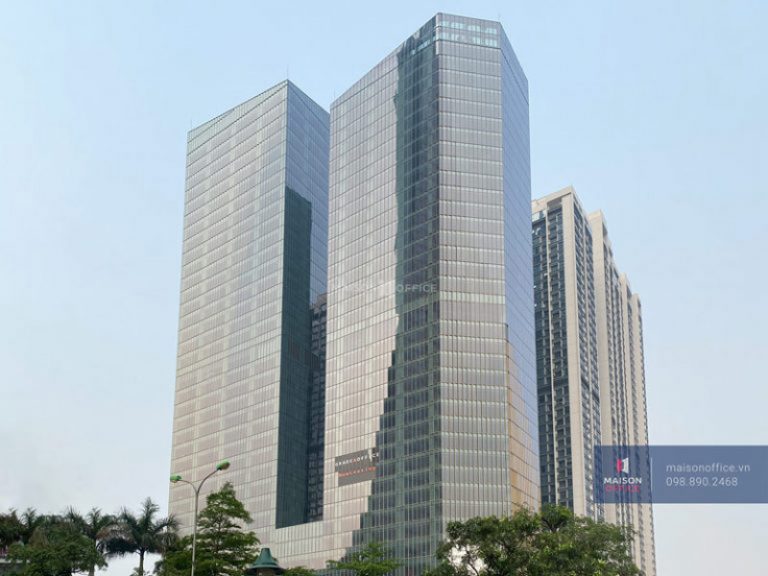
8.3 Capital Place Twin Towers – Hanoi
Capital Place, an A-grade office rental space located on Lieu Giai Street in Hanoi, spans over 128,000 m2 of floor space, making it one of the first skyscrapers in Hanoi to receive a LEED Gold certification.
The building consists of two 37-story towers resting on a shared podium with three basement levels. Using glass as the main material, Capital Place can save up to 13% of electrical energy compared to other buildings.
Notably, Capital Place is situated in the city center, with convenient transportation infrastructure and surrounded by amenities such as shopping centers, five-star hotels, and government offices.
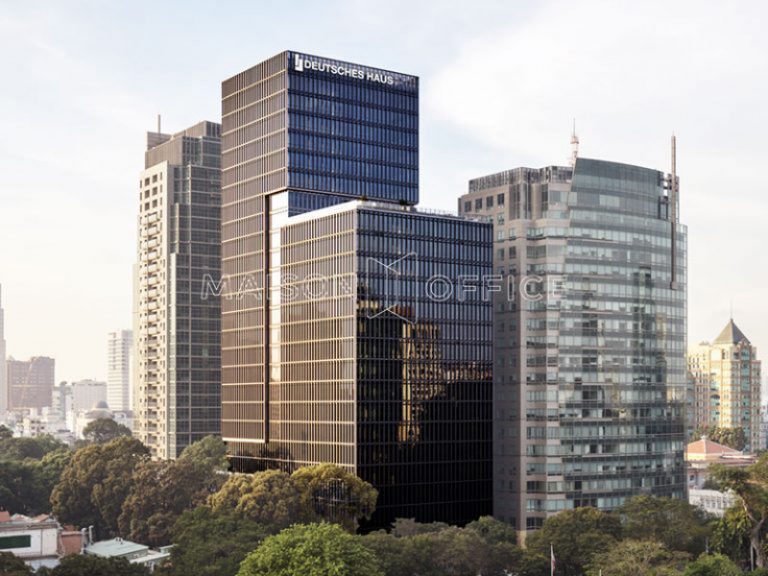
8.4 Deutsches Haus – Ho Chi Minh City
Deutsches Haus is among the few office skyscrapers in Southeast Asia to achieve a LEED Platinum certification. Located on Le Duan Street, one of the most beautiful streets in Ho Chi Minh City, Deutsches Haus consists of 25 above-ground floors and 4 basement levels. It serves as a workplace for many administrative bodies, large business organizations of Vietnam, and the Federal Republic of Germany in Saigon.
The building materials used are highly environmentally friendly, ensuring maximum energy savings. This is made possible by the meticulous calculations of the building’s architects to ensure the project’s compatibility with the local climate conditions.
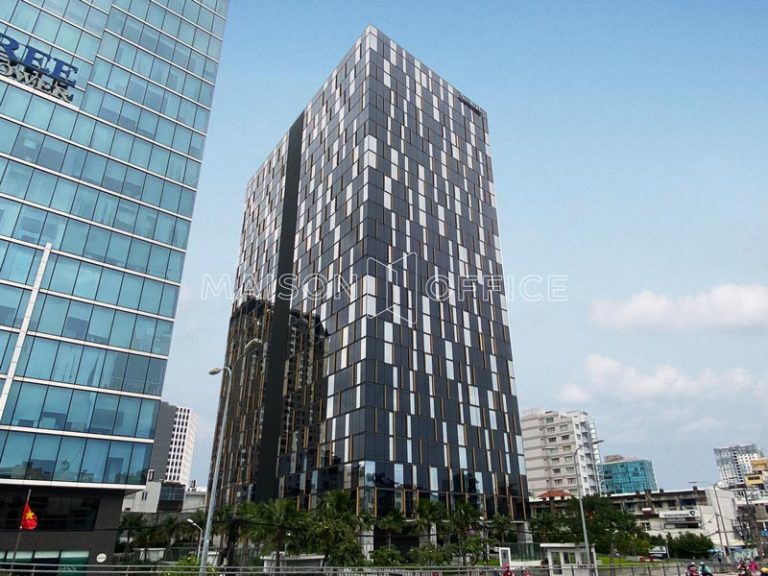
8.5 ETOWN Central – District 4, Ho Chi Minh City
ETOWN Central in District 4, located in the central part of District 4, is one of the leading office buildings in Ho Chi Minh City. With modern architecture and flexible workspace, ETOWN Central is an ideal destination for companies and businesses seeking an office location in a convenient, easily accessible area within the city.
Standing out in the heart of District 4, ETOWN Central comprises 26 above-ground floors, a ground floor, and 5 basement levels. The building has become a sought-after location for green, sustainable office rentals by many businesses.
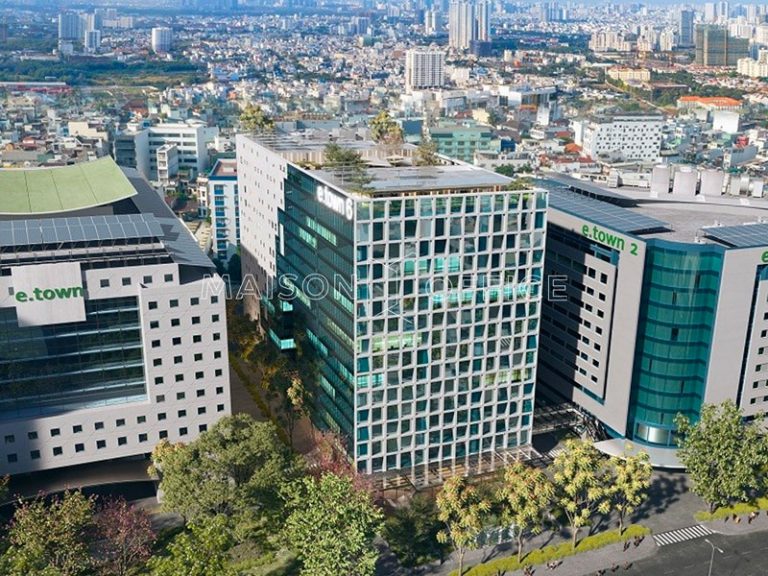
8.6 Etown 6 – Tan Binh District, Ho Chi Minh City
Etown 6 in Tan Binh District, conveniently located near the airport and major industrial parks, is a perfect choice for domestic and international businesses. The building offers flexible office space, high-class amenities, and professional services, strongly supporting the growth and success of businesses.

Editor and content team manager at Maison Office.
With over 5 years of experience in consulting and extensive content editing in the real estate services and interior design field. Sharing valuable information with customers, partners, and attracting millions of views.