The lessor: Definition, Types & Examples in real estate

In the complex world of real estate, specialized terms often make us feel strange and difficult to understand. As someone who wants to learn about the real estate market, you have certainly heard the term “Lessor”, but do you really know “What is Lessor?” and the real meaning behind it?
Table of Contents
- 1. What is Lessor?
- 2. Lessor vs Lessee: What’s the Difference?
- 3. What roles does Lessor have?
- 4. Common reducer types
- 5. Discover the lessor’s rights – What is Lessor?
- 6. Lessor’s transaction implementation process – Lessor
- 7. What obligations must the lessor – Lessor perform?
- 8. Maison Office – Specializing in consulting and leasing professional offices
1. What is Lessor?
A lessor is a person or entity that owns real estate property (such as a house, an apartment, or a piece of land) and allows others to use that property under a lease.
The lessor is often called the owner or landlord, and has the right to license the tenant (called the lessee) to use the property for a specified period of time and according to the conditions agreed in the lease. Lessor is responsible for providing the property in good condition, carrying out necessary repairs and collecting rent from lessee as agreed.
What is Lessor in the field of office leasing?
Suppose there is an individual, A, who wants to open a new store near a shopping mall, but cannot afford to construct or purchase a new building. A knows that an individual or business, B, owns a building near a shopping center and is looking for a tenant.
In this case, A is considered the lessee, while B is the lessor. By signing a lease contract, B transfers ownership or the right to use the asset to A. Meanwhile, A pays monthly rent to B.
In the financial sector, if you are the grantor of capital, you are called a lessor, while if you are the recipient of capital, you are a lessee. Another example, if you own a house and rent it out, you are also considered a lessor.
Lessors are not limited to individuals, but can also apply to legal entities. Another synonym for leasing companies is “leasing company.” Lessor is the party that provides assets (such as real estate, equipment, machinery, etc.) for the lessee to use for a specified period of time, in order to earn rental income.
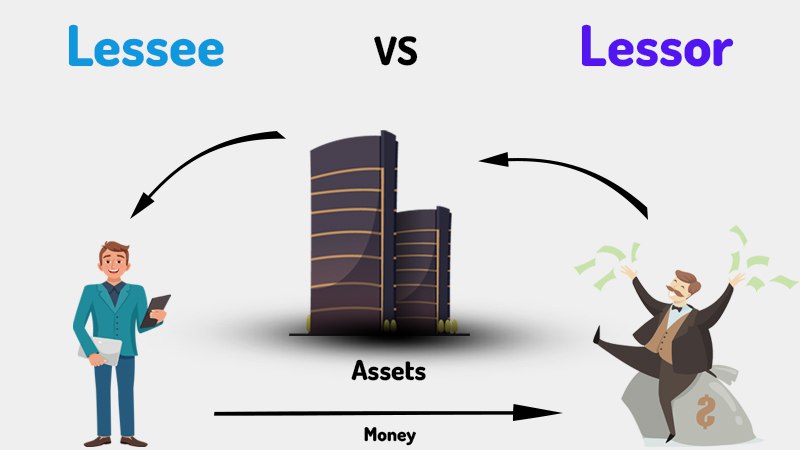
2. Lessor vs Lessee: What’s the Difference?
The terms “lessor” and “lessee” refer to the two parties involved in a lease agreement, each with distinct roles:
- Lessor: This is the party that owns the property or asset being leased out. The lessor grants the right to use the property to the lessee for a specified period, in return for payment. Lessors can be individuals or entities, such as companies or organizations that rent out real estate, vehicles, or equipment.
- Lessee: The lessee is the party that obtains the right to use the property or asset under the lease agreement. The lessee agrees to make payments to the lessor for the duration of the lease term and is responsible for maintaining the condition of the property, depending on the terms of the lease.
In summary, the lessor provides the property for lease, while the lessee pays to use the property for a certain time. Their relationship is governed by the lease agreement, which outlines the terms, conditions, and obligations of both parties.
3. What roles does Lessor have?
Below are some important roles of the lessor (lessor):
– The lessor is responsible for granting basic ownership of the asset to the lessee, allowing the lessee to use the asset according to the conditions and circumstances agreed between the two parties.
– The lessor commits to ensuring that throughout the lease period, the lessee continues to enjoy ownership of the asset, as long as payments for that asset are made according to the agreement. During the lease period, the lessee has no interruption in ownership of the asset.

– Before signing the lease contract, the lessor must disclose any defects in the property. Failures can be of two types: latent failures and easily discernible failures. Latent failures are problems that cannot be detected through regular inspection. Meanwhile, visible failures are problems that can be easily recognized through regular inspection.
– Any costs that the lessee must pay to preserve the leased property will be reimbursed by the lessor. However, the lessee will be responsible for all costs related to regular maintenance and operations.
In short, the lessor’s role is to ensure that the property lease goes smoothly, protecting the interests of both the lessor and the lessee.
4. Common reducer types
Lessor is a business term commonly used in finance and real estate. There are many popular reducer types:
– Manufacturer or Supplier: This is the lessor that manufactures the assets it rents out, or is a supplier that has agreed with the rental company to provide competitive rates.
Common reducer types
– Banks: Banks sometimes own rental companies themselves and extend rental offers to their existing customers.
– Independent lessors: These are lessors that completely specialize in leasing. They may operate in specific industries or asset classes, or even operate in a variety of sectors.
5. Discover the lessor’s rights – What is Lessor?
Lessor is a person or organization that legally owns an asset (such as real estate, equipment, machinery, etc.) and allows others to use that asset through signing a lease contract. The lessor is the person who provides the property for lease and is responsible for managing, maintaining and protecting the property during the lease period.
Below are the important benefits of the lessor:
– Income from rental: One of the main benefits of the lessor is to receive income from leasing its property. By allowing others to use the property for a specified period of time in exchange for rent, lessors generate significant rental income.
Discover the lessor’s rights – What is Lessor?
– Right to control and own the asset: The lessor retains the right to control and own the asset throughout the lease period. Even though the asset is used by the lessee, ownership remains with the lessor until the lease ends.
– Right to specify lease conditions: The lessor has the right to specify the conditions, terms and commitments in the lease contract. This includes the rental price, rental period, rights and obligations of both parties during the property rental process
– Right to inspect property condition: Lessor has the right to periodically inspect the property condition to ensure that it is still properly preserved and used. This helps ensure the property is not damaged or devalued during the rental period.
– Right to choose the lessee: The lessor has the right to choose the appropriate lessee to use their assets. This decision is often based on the need to use the asset, the ability to pay and the reputation of the lessee.
– Right to recover property: In case the lessee violates the contract or does not pay rent on time, the lessor has the right to recover the property according to the provisions of the contract or according to the law.
– Right to improve the property: Lessor may be allowed to improve, upgrade, or replace the property after a lease period, depending on the terms of the contract.
Thanks to asset leasing, lessors have the opportunity to profit from owning assets without having to bear the risks and daily management responsibilities like lessees. However, there may also be certain risks, such as the risk of the asset being damaged or losing value during the lease.
6. Lessor’s transaction implementation process – Lessor
The lessor’s transaction process usually includes the following steps:
– Identify rental properties: Lessor identifies the properties they want to rent. This could be real estate, machinery, equipment, aircraft, boats or any asset that the lessor owns and wants to let others use.
– Determine lease terms and conditions: Lessor determines the terms and conditions that the lessee needs to comply with when using the asset. These terms include the rental price, rental period, special conditions, and other requirements related to the use of the property.
– Lease agreement: The lessor and lessee negotiate and agree on the terms and conditions in the lease contract. The contract needs to be written clearly and accurately, including the commitments and rights of both parties.
Lessor’s transaction execution process – Lessor
– Asset inspection: Before the transaction is made, the lessor may request to inspect the assets to ensure their condition and functionality. This can ensure that the property is in good condition and ready for use.
– Execute the transaction: After the contract is signed and assets are inspected (if any), the transaction is performed. The asset is transferred to the lessee and the lessor receives rent according to the agreed terms.
– Supervising and maintaining the property: During the rental period, the lessor is responsible for supervising and maintaining the property. They can perform routine maintenance, servicing and inspections to ensure assets are always in good working order.
– Meet the lessee’s requirements: During the lease period, the lessor must meet the lessee’s reasonable requirements and needs related to the asset.
– End of the lease contract: When the lease contract ends, the lessor may have the right to recover the property or continue to negotiate with the lessee about contract extension or new conditions.
The lessor’s transaction execution process may vary depending on the type of asset and the specific industry in which the lessor operates.
7. What obligations must the lessor – Lessor perform?
The Lessor must fulfill a number of obligations and responsibilities to ensure the rights of himself and the lessee during the leasing transaction. Below are some main obligations of the lessor:
– Providing rental assets: Lessor must provide the assets agreed upon in the contract for the lessee to use according to the agreed time and conditions.
– Providing complete and accurate information: Lessor is obliged to ensure that the rental property meets full functionality and is safe during use. They must ensure that the property has no significant problems that would affect its use by the lessee.
What obligations must the Lessor – Lessor perform?
– Property maintenance and repair: Lessor is responsible for maintaining and repairing the property throughout the rental period, ensuring that the property still operates well and does not cause obstacles for the lessee to use.
– Collect rent on time: The lessor must collect rent from the lessee on time and confirm the correctness of payments.
– Comply with the terms of the contract: Lessor must comply with all terms and conditions agreed in the lease contract, including the lease term, price, rights and obligations of both parties.
– Dispute resolution: If a dispute arises between the lessor and the lessee related to the lease of the property, the lessor needs to participate and resolve these issues in a reasonable and fair manner.
These obligations ensure that the lessee has rights and ensures fairness in the process of leasing assets from the lessor.
8. Maison Office – Specializing in consulting and leasing professional offices
Maison Office is proud to be one of the leading units in Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi providing professional and reputable offices for rent. We offer a variety of office types from Grade A, Grade B to Grade C, and also provide cheap office packages and full office packages depending on your needs. With a prime location spread throughout the districts, Maison Office meets all business requirements.
Maison Office Company – Specializing in consulting and leasing professional offices
If you need to rent a professional office, please contact Maison Office immediately for free consultation and field survey.
Detailed information about the term “lessor?” as well as the roles and rights of the rental service provider mentioned above. Hopefully through this article, you will have a clearer view of the term Lessor in contracts and the necessary information before deciding to rent an office or use other services.

Editor and content team manager at Maison Office.
With over 5 years of experience in consulting and extensive content editing in the real estate services and interior design field. Sharing valuable information with customers, partners, and attracting millions of views.